in recent years, as one of the hot topics, global warming has attracted wide attention. temperature participates in many aspects of plant growth and development, and has a very important impact on agricultural production. high temperature stress can lead to elongation of the stalk, early flowering and severe reduction of crop yield. therefore, the study of the mechanisms of temperature sensing and signal transduction will provide theoretical basis for future molecular breeding.
on may 8, professor li jia, dean of school of life sciences at lanzhou university, published a research paper entitled "tcp transcription factors associate with phytochrome interacting factor 4 and cryptochrome 1 to regulate thermomorphogenesis in arabidopsis liana" in iscience, a new cell press journal. in this study, the researchers found that high temperature can promote the expression of a tcp gene that encodes a transcription factor, which enhances the transcriptional activity of pif4 by associating with pif4.
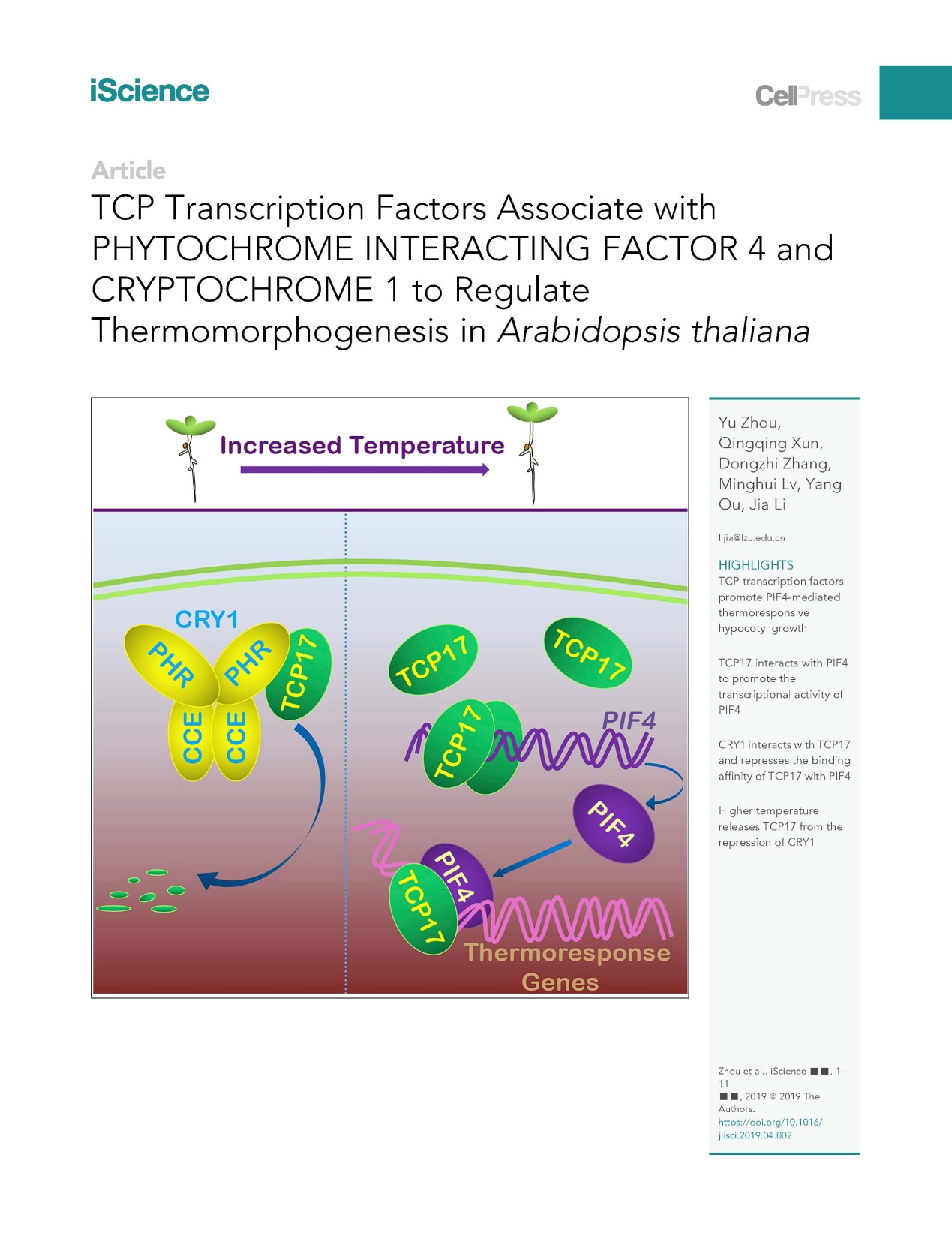
zhou yu, a ph.d. student of school of life sciences, is the first author of this paper and professor li jia is the corresponding author. the school of life sciences at lanzhou university is the first unit of this paper. this research is supported by the ministry of education and the national natural science foundation of china.
